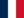
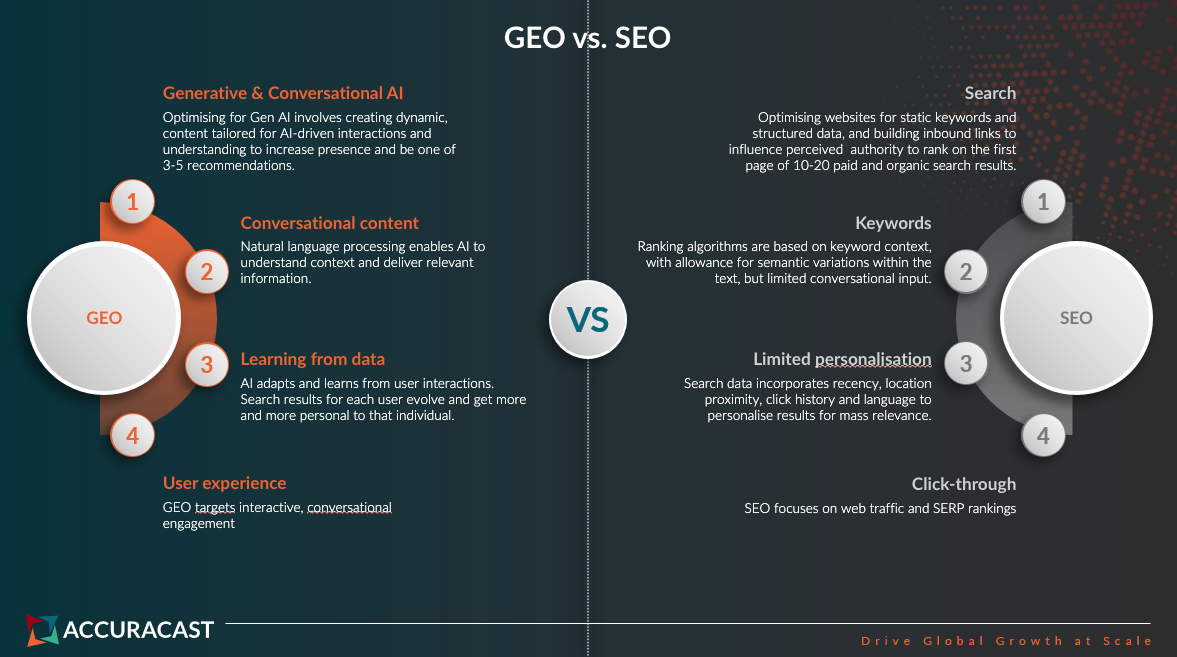
The perspective is that the introduction of AI overview in search will have a high impact on businesses and people, especially in terms of traffic and processes for search engine optimisation (SEO).
Recent data has shown a decrease in the amount of traffic referred from search results pages when AI Overviews were introduced. This decrease in traffic is nothing new in the world of digital marketing. According to the “Zero-Click Search Study” from Sparktoro, for every 1,000 Google Searches in the EU, only 374 clicks go to the open web, and in the USA, this number is 360.
With the increased proliferation of AI search, many believe there will be an even greater drop in traffic, with an increase in ‘zero click‘ results, especially for keywords with less specific intentions, that is, for searches at the top of the funnel.
The logic is simple: the answer given by the AI to these more general questions will probably satisfy users, reducing the chances of them clicking and going to your website. Considering that many businesses rely on online traffic and visibility to generate conversions and sales, there is a discussion of how GEs have a very high potential to affect the economy of those who work with content in general.
GEO was created to help businesses deal better with the changes we are going through, especially when the landscape is shifting rapidly and there isn’t much certainty about what the next steps will be.
In the words of the Princeton study:
“To address this, we introduce Generative engine optimisation (GEO), a new paradigm to help content creators improve the visibility of their content in GE responses through an optimisation framework to optimise and define visibility metrics”