| Feature |
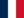
SEO |
GEO |
| Interface |
Human searchers directly interact with traditional search tools (e.g., Google search bar). |
Chatbot and conversational AI interfaces (e.g., ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot), which provide synthesised answers. |
| Output Format |
Ranked lists of web pages, designed to drive clicks to websites. |
Synthesised, direct answers, summaries, or new content generated by AI, often without a direct click to the source. |
| Referral Traffic |
Primarily drives direct website traffic through organic clicks. |
Often results in zero-click answers, reducing the need for direct website visits. |
| Content Input |
Primarily keywords and 2–4 word phrases. |
Natural language questions, prompts, and complex queries. |
| Authority Signals |
Backlinks, domain authority, keyword usage, and technical soundness. |
Factual accuracy, citations, and inclusion in reliable training or RAG data. |
| Number of Results |
Typically 10 ranked organic results with enhanced listings. |
Usually a single answer or 3–5 curated suggestions. |
| Changeability |
Updates every few months via algorithm changes. |
Rapid evolution with frequent LLM and AI updates. |
| Personalisation |
Limited personalisation via history and location. |
Highly personalised through conversation context and preferences. |
| Metrics / Measurement |
Traffic, rankings, CTR, conversions, bounce rate. |
AI mentions, factual accuracy, training data presence, query completion. |
| Data Sources & Indexing |
Web crawling via robots.txt and sitemaps. |
Model training data, RAG corpuses, API-based retrieval. |
| Crawling & Updating |
Continuous crawling and indexing. |
Periodic model updates; RAG pulls real-time data where available. |
| Query Processing |
Keyword and semantic matching. |
Intent recognition and contextual reasoning. |
| Algorithms |
Core Web Vitals, E-E-A-T, link analysis, spam scoring. |
Factual integrity, coherence, relevance, and quality-based evaluation. |