While people can search for almost everything through the search engines, a recently conducted study has found that certain terms are used very commonly with each query.
These terms are not queries in themselves, but are modifiers to the queries. They are, ‘Who’, ‘What’, ‘Where’, ‘When’, ‘Why’ and ‘How’.
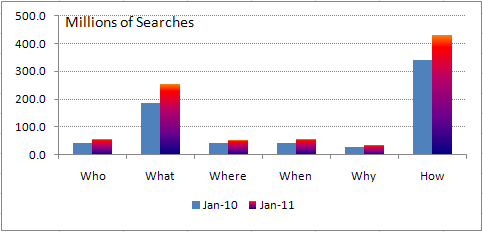
Researchers at comScore found that the use of these modifiers has grown significantly between January 2010 and January 2011.
Number of searches on most popular modifiers in Jan 2010 v Jan 2011
Who – This question is generally asked with an ‘is’ ‘are’, ‘was’, or ‘were’ attached to it. In January 2011, 57 million searches by 21 million searchers in the U.S. searched questions with ‘who’. The most common question with ‘Who’ are, ‘Who is searching for me’, ‘Who is looking for me’, ‘Who is looking at my Facebook profile’ and ‘Who am I’.
What – This question is usually attached with an ‘is’, ‘does’, ‘are’, ‘was’ or ‘were’. 253 million searches by 52 million people were conducted with this modifier in the U.S. in January 2011.
Where – The most common questions here are, ‘Where is’, ‘Where are’, ‘Wheres’, ‘Where’s’ and ‘Where was’. The term ‘where’ had 52 million searches from 29 million searchers in the U.S. in January 2011.
When – This question is asked with an ‘is’, ‘was’, ‘did’ and ‘does’. It is almost as common as ‘where’ with 54.8 million searches by 21 million searchers in the U.S. in January 2011. The most common ‘When’ questions are about upcoming events, holidays and festivals. If publishers can keep track of when these question are likely to be asked, they can reach their target audience easily.
Why – The most common questions here are ‘Why do’, ‘Why is’, ‘Why are’, ‘Why did’ and ‘why does’. This question has 33 million searches from 13 million searchers in January 2011.
How – This is the most common search term modifier by far, with 431 million searches by 71 million searchers. It is attached with a ‘to’, ‘do’, ‘much’, ‘many’ and ‘does’. Of this, ‘How to’ had over 253 million questions in January 2011, up by 35% in 1 year.
Since it has been found that these searches continue to increase, at a rapid pace, publishers and marketers can make good use of these modifiers to find their target audiences and to improve engagement with them.
About the Author
Farhad is the Group CEO of AccuraCast. With over 20 years of experience in digital, Farhad is one of the leading technical marketing experts in the world. His specialities include digital strategy, international business, product marketing, measurement, marketing with data, technical SEO, and growth analytics.